Introduction
The initial project for these pages was to draw the Star Maps by Constellation, similar to the ones found on the International Astronomical Union's web site, but that I wanted more complete with respect to the Flamsteed and Bayer/Lacaille star designations.
The coordinates for the constellations boundaries were one of the first requirements, which led to the Constellation Boundaries page. Unable to find a complete set of Flamsteed and Bayer star designations, I resorted to Morton Wagman's book Lost Stars [1] and ended up putting Flamsteed's Catalog in machine-readable form.
This triggered my interest in digitizing other historical catalogs, examining relashionships between them, and drawing star maps. Two pages are dedicated to each catalog, the second one featuring star maps of the catalog in its own coordinate systems.
I try to introduce each catalog with background historical information in order to make the pages more pleasant and hopefully instructive to read. However, I'm not a historian of astronomy and a specialist might frown at some statements or notice gaping holes. I'm open to suggestions for improvement.
Beyond that, I have made a special effort to present only verifiable, objective information. For instance, the machine-readable versions of the catalogs can be compared to the originals, for which I give my sources. I particularly avoid speculating about the modern designations that could be assigned to historical catalog entries. There is already enough uncertainty and confusion in that domain. The maps superimpose modern catalog stars to historical ones, without explicit association between them.
For each catalog, I have attempted to capture as accurately as possible all the content that can be represented in simple structured data files. I have patiently copied and verified the raw data, but there may still be errors (there always are…) and I may have made arbitrary choices. I would appreciate the feedback if an error is detected.
One of my goals is to facilitate the analysis of catalog data and their cross-references by computer programs. The files should be readily machine-readable. For this reason, I have adopted formats and file descriptions compatible with the conventions for catalogue descriptions of the VizieR service, rather than invent my own. As a bonus, the data files can be subjected to some automatic validation using the Anafile package.
Several reprints of historical catalogs contain star identifications made by their authors (e.g., Dreyer, Baily, Flamsteed). I capture these in their own cross_*.dat files separate from the original catalog data. In accordance with the objectivity goal mentioned above, I capture them in their raw form, without for instance trying to convert obsolete Bayer designations or adding modern catalog references.
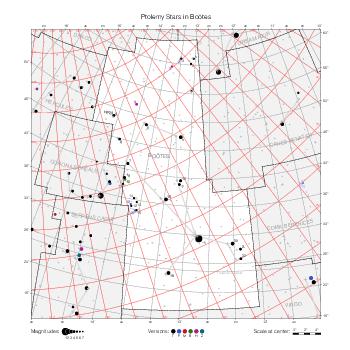
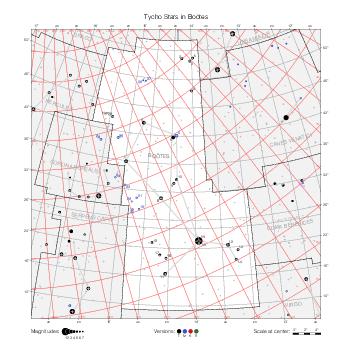
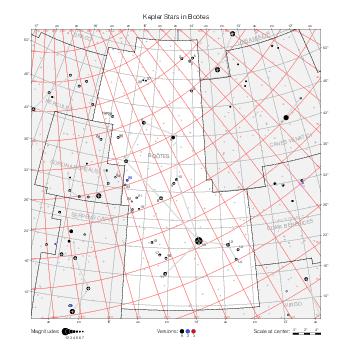
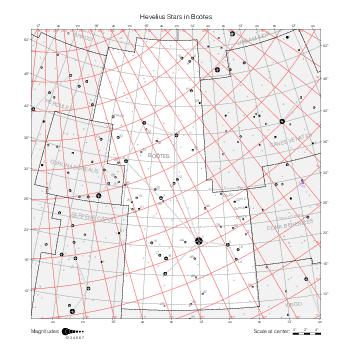
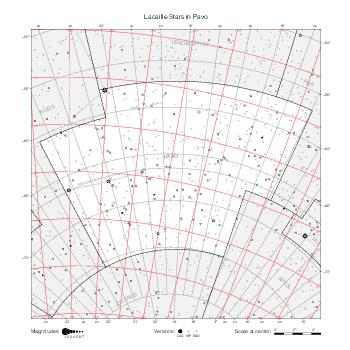
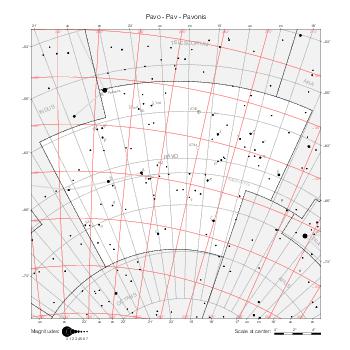
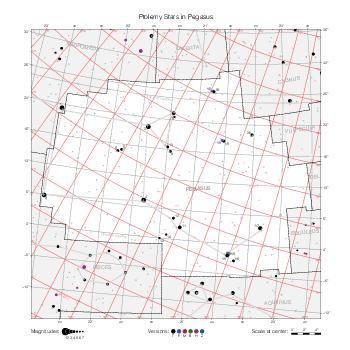
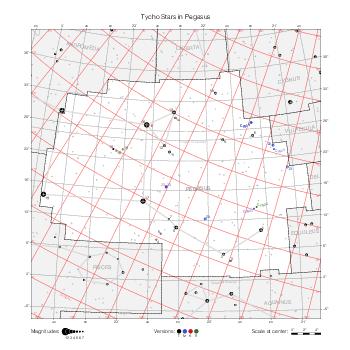
Map features
This section describes the common features of the star maps associated with historical catalogs.
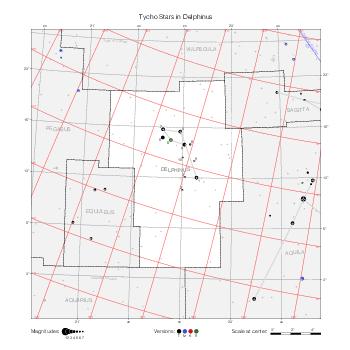
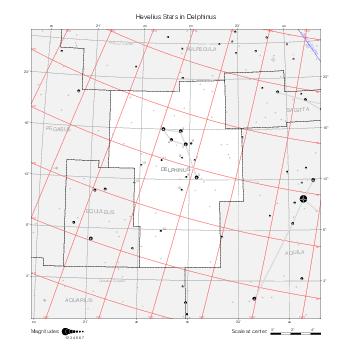
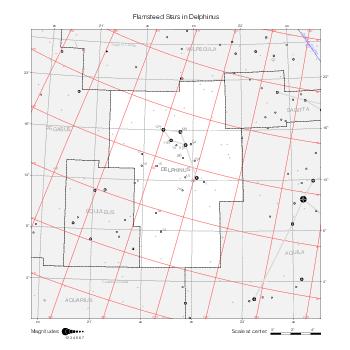
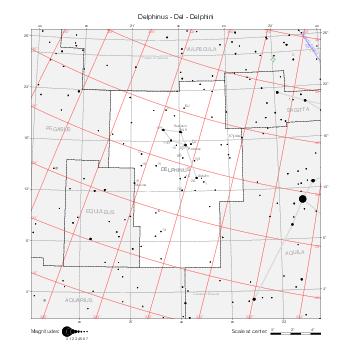
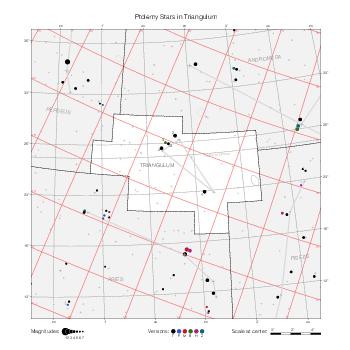
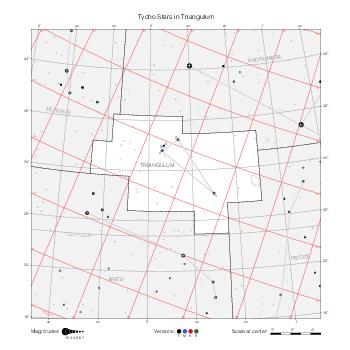
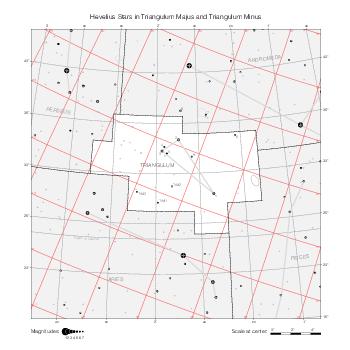
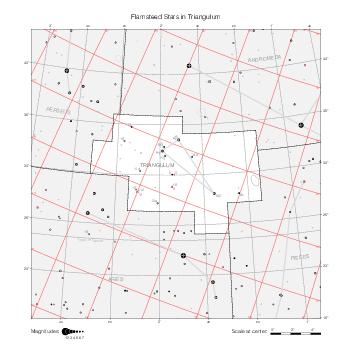
Representation of catalog stars
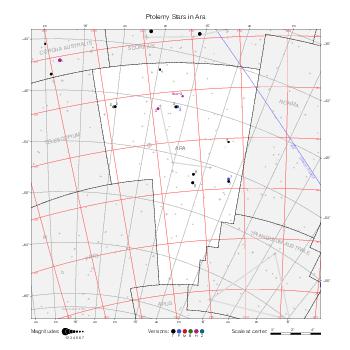
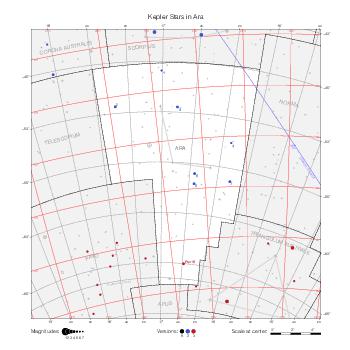
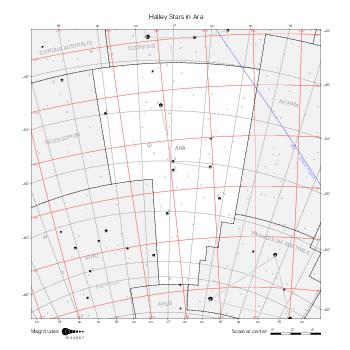
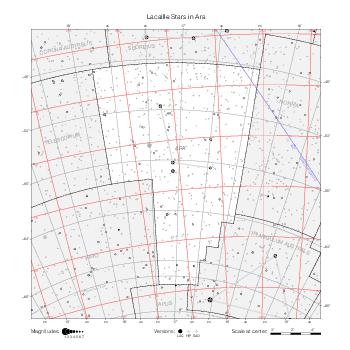
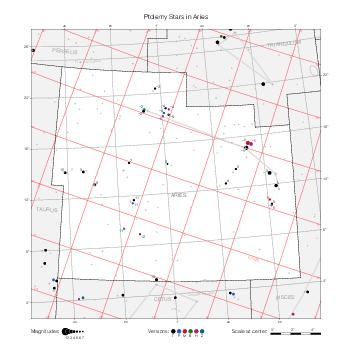
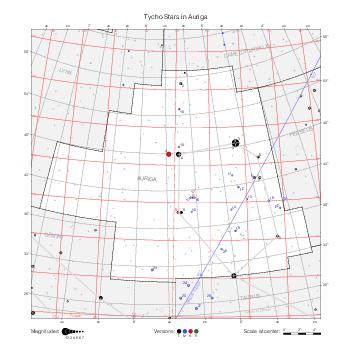
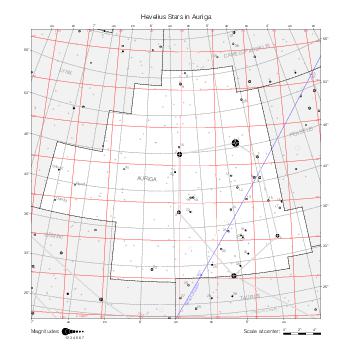
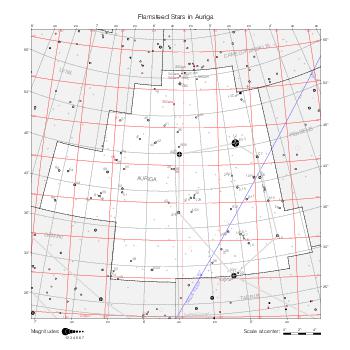
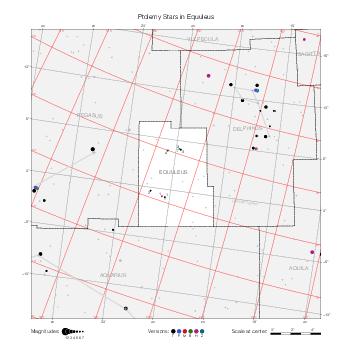
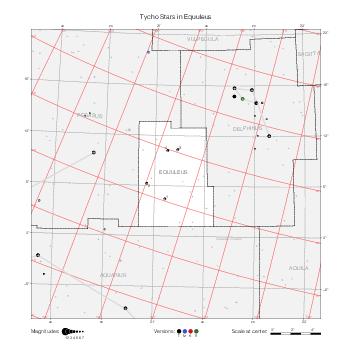
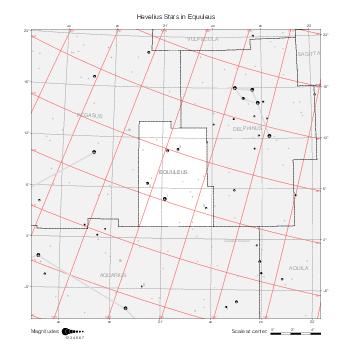
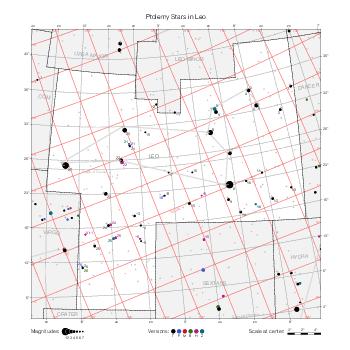
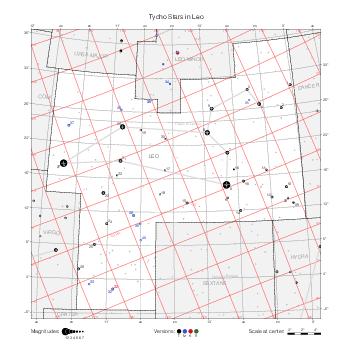
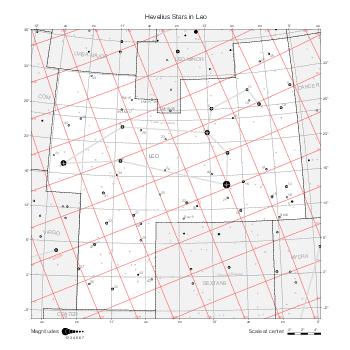
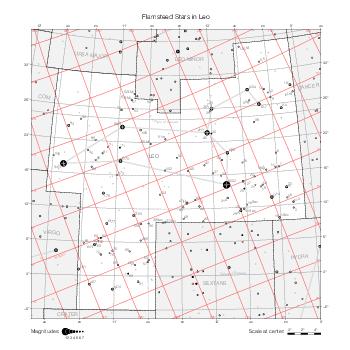
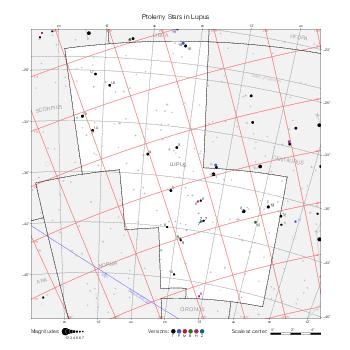
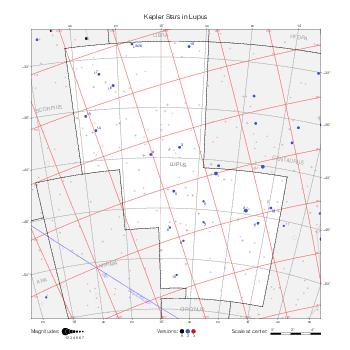
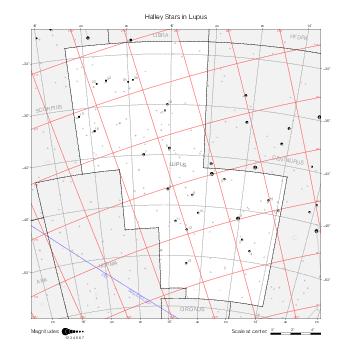
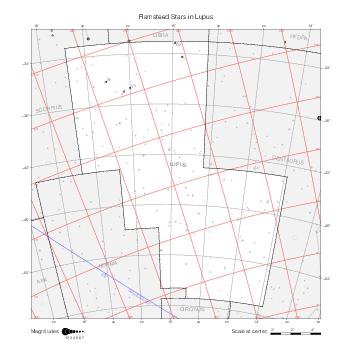
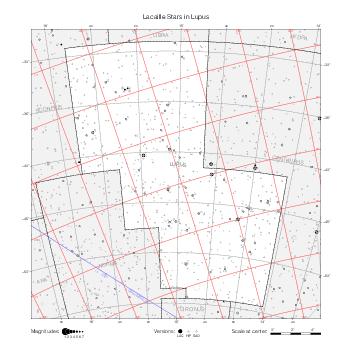
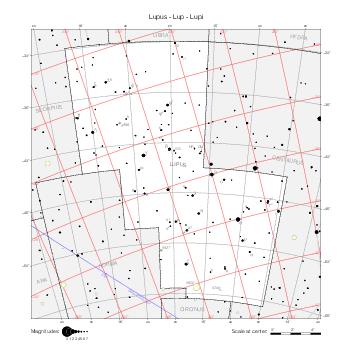
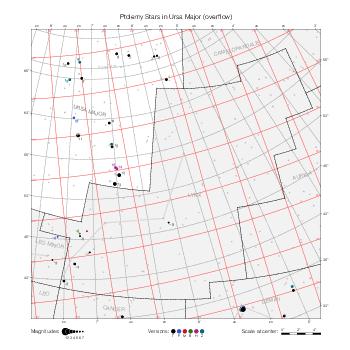
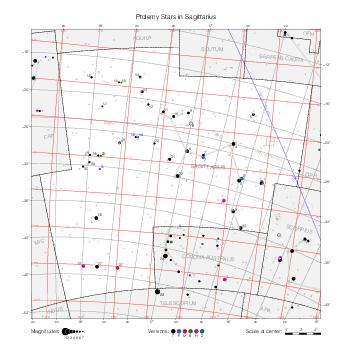
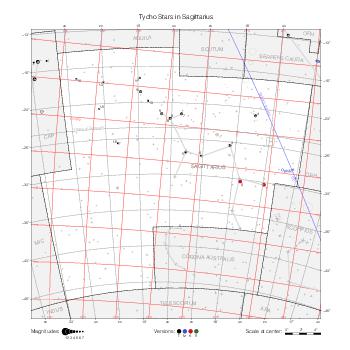
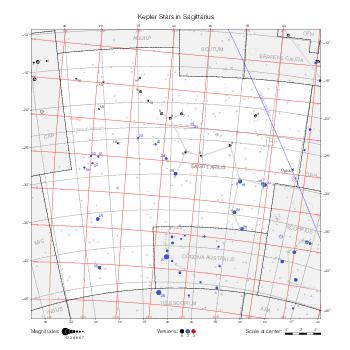
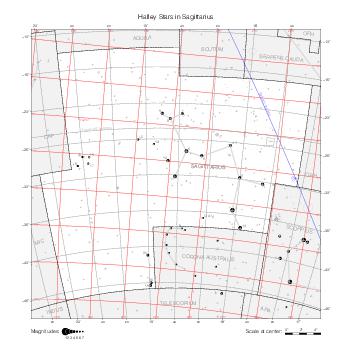
The maps represent catalog entries by black or colored disks for stars and light disks with a dotted border for nebulous objects. For stars, the size of the disk varies with the magnitude assigned by the catalog. For nebulous objects, the size corresponds to some fixed, arbitrary magnitude value.
Different versions of a given catalog may be represented on the same maps, using different colors to distinguish versions from each other. In that case, a legend describes the color to version mapping. For some catalogs, corrected star positions or designations are represented in red.
Star designations
Star designations according to the catalog under study are represented. They usually consist of a constellation abbreviation and a sequence number within the constellation.
On maps by constellation, the designation is shown for stars assigned by the catalog to the constellation(s) under consideration and stars from neighboring constellation that fall within its modern boundary. The constellation abbreviation is omitted if it matches the constellation covered by the map.
On other maps, the constellation abbreviation is shown when the constellation assigned by the catalog differs from the modern constellation containing the star.
Reference stars
Reference stars and NGC objects are represented by thin asterisks (for stars) or simplified icons. Star positions, adjusted to the catalog's epoch according to their proper motion and precessed to the catalog's equinox, come from the Hipparcos Catalogue and/or the SAO Catalogue.
For most catalogs, the reference stars are the ones shown on the reference maps and represented by 4-point asterisks. For more recent catalogs (such as Lacaille's), this star set doesn't suffice and the whole Hipparcos and SAO catalogs, up to some cutoff magnitude, are shown. The Hipparcos and SAO stars are represented by incomplete 4-point asterisks that, when combined, look like complete 4-point asterisks as long as the Hipparcos positions and magnitudes match. This allows fainter stars found in only one of these catalogs to be represented.
Other features
Modern constellation boundaries are represented for reference. The maps are framed around these boundaries exactly like the reference maps to facilitate the comparison of catalogs to each other or to the reference.
Equatorial, ecliptic, and galactic coordinate lines and points are represented. The equatorial and ecliptic coordinate system correspond to the catalog's equinox and the obliquity of the ecliptic is computed according to the IAU 2006 precession model for the catalog's equinox.
Star maps by constellation
For convenience, the following scrollable table provides direct access to the star maps by constellation according to most of these catalogs, otherwise scattered across multiple pages. I use them frequently to compare catalogs to each other or to the reference (in the last column).
Star maps by hemisphere
The following table gathers the maps by hemisphere. The southern maps for Halley's and Lacaille's catalogs are drawn at different scales.
| Ptolemy | Tycho | Kepler | Halley | Hevelius | Flamsteed | Lacaille | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ptolemy | Tycho | Kepler | Halley | Hevelius | Flamsteed | Lacaille | |
| Northern | 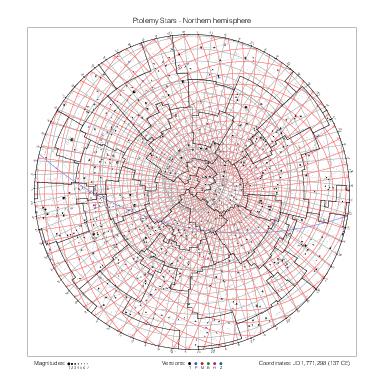 |
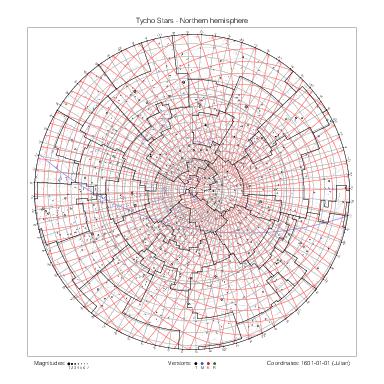 |
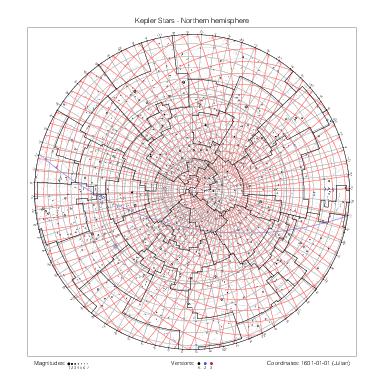 |
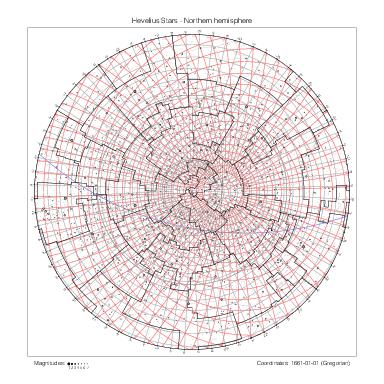 |
 |
||
| Southern |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
References
[1] Morton Wagman, Lost Stars, McDonald & Woodward Publishing Company, Blacksburg, Virginia, 2003.